|
|
|
1.
|
The hybridization of the central atom in I3–
is:
A) | sp | B) | sp2 | C) | sp3 | D) | dsp3 | E) | d2sp3 |
|
|
|
2.
|
Which of the following molecules contains a central atom with
sp2 hybridization?
|
|
|
3.
|
The hybridization of the B in BH3 is sp3.
|
|
|
4.
|
The hybridization of a molecule is measured to determine the shape of the
molecule.
|
|
|
5.
|
Which of the following statements is (are) incorrect? | I. | The hybridization of boron in
BF3 is sp2. | | II. | The molecule XeF4 is nonpolar. | | III. | The bond order of
N2 is three. | | IV. | The molecule HCN has two pi bonds and two sigma bonds. | | |
A) | All four statements are correct. | B) | II is incorrect. | C) | I and IV are
incorrect. | D) | II and III are incorrect. | E) | II, III, and IV are
incorrect. |
|
|
|
6.
|
Larger bond order means greater bond strength.
|
|
|
7.
|
When an electron pair is shared in the area centered on a line joining the
atoms, a s (sigma) bond is formed.
|
|
|
8.
|
According to MO theory, F2 should be diamagnetic.
|
|
|
9.
|
Which of the following electron distributions among the molecular orbitals best
describes the NO molecule? | s2s | s2s* | p2py=p2px | s2pz | p2py*=p2px* | s2pz* | | | | | | |
A) | 2
2
4
2
4
2 | B) | 2
2
4
2
4
1 | C) | 2
2
4
1
3
0 | D) | 2
2
4
2
2
0 | E) | 2
2
4
2
1
0 |
|
|
|
10.
|
Which of the following statements about the CO32–
ion is false?
A) | The orbitals on the carbon atom are sp2
hybridized. | B) | The ion is expected to be diamagnetic. | C) | The C–O bonds are different
lengths. | D) | The ion has a total of 24 electrons. | E) | All the above statements are
true. |
|
|
|
11.
|
Consider the benzene molecule. Which of the following statements about the
molecule is false?
A) | All six C–C bonds are known to be equivalent. | B) | Each carbon atom is
sp2 hybridized. | C) | The localized electron model must invoke
resonance to account for the six equal C–C bonds. | D) | It has delocalized
pi bonding in the molecule. | E) | The pi bonds of carbon involve
sp2 orbitals. |
|
|
|
12.
|
Consider three molecules – A, B, C. Molecule A has a hybridization of
sp3. Molecule B has two more effective pairs (electron pairs around the central
atom) than molecule A. Molecule C consists of one s bond and two p bonds. Give the molecular structure, hybridization, bond angles, and an
example for each molecule.
|
|
|
13.
|
A(n) __________ molecular orbital is lower in energy than the atomic orbital of
which it is composed.
|
|
|
14.
|
In general, the density of a compound as a gas is closer in value to that of the
compound as a liquid than the density of the compound as a liquid is in value to that of the compound
as a solid.
|
|
|
15.
|
The freezing point of helium is –270°C. The freezing point of xenon
is –112°C. Both of these are in the noble gas family. Which of the following statements is
supported by these data?
A) | Helium and xenon form highly polar molecules. | B) | As the molecular
weight of the noble gas increases, the freezing point decreases. | C) | The London
dispersion forces between the helium molecules are greater than the London dispersion between the
xenon molecules. | D) | The London dispersion forces between the helium molecules are less than the London
dispersion forces between the xenon molecules. | E) | None of these. |
|
|
|
16.
|
Intermolecular forces are weaker than intramolecular bonds.
|
|
|
17.
|
Methane (CH4) exhibits stronger hydrogen bond interactions than
ammonia (NH3).
|
|
|
18.
|
Liquids with large intermolecular forces tend to have high surface
tension.
|
|
|
19.
|
Table salt and table sugar are both crystalline solids.
|
|
|
20.
|
Atomic solids generally have low melting points.
|
|
|
21.
|
Which of the following statements about steel is false?
A) | It contains carbon atoms in the holes of its iron crystals. | B) | The presence of
carbon-iron bonds in the alloy make steel harder and stronger than pure iron. | C) | Pure iron is
relatively soft and ductile because it lacks directional bonding. | D) | The amount of carbon
directly affects the properties of steel. | E) | All of these are
true. |
|
|
|
22.
|
Steel is a substitutional alloy.
|
|
|
23.
|
Which of the compounds below is an example of a network solid?
A) | S8(s) | B) | SiO2(s) | C) | MgO(s) | D) | NaCl(s) | E) | C25H52(s) |
|
|
|
24.
|
Ice is a molecular solid.
|
|
|
25.
|
Which of the following has the highest melting temperature?
|
|
|
26.
|
Water sits in an open beaker. Assuming constant temperature and pressure, the
rate of evaporation decreases as the water evaporates.
|
|
|
27.
|
Water sits in an open beaker. Assuming constant temperature and pressure, the
vapor pressure of the water decreases as the water evaporates.
|
|
|
28.
|
The normal boiling point of liquid X is less than that of Y, which is less than
that of Z. Which of the following is the correct order of increasing vapor pressure of the three
liquids at STP?
A) | X, Y, Z | B) | Z, Y, X | C) | Y, X,
Z | D) | X, Z, Y | E) | Y, Z, X |
|
|
|
29.
|
Which of the following has the highest boiling point?
A) | chalk (calcium carbonate) | B) | ice (water) | C) | window cleaner
(ammonia) | D) | motor oil (hydrocarbon chains) | E) | helium gas inside a party
balloon |
|
|
|
30.
|
The process of changing from a vapor to a liquid is vaporization.
|
|
|
31.
|
Make a sketch to show the hydrogen bonding between two acetic acid molecules
(HC2H3O2).
|
|
|
32.
|
Explain why water boils at a lower temperature up in the mountains versus at sea
level. Include at least one microscopic drawing in your explanation.
|
|
|
33.
|
Which of the following compounds is expected to have the
HIGHEST melting point?
A) | CH3OCH3 | B) | CH3CH2OH | C) | CH3CH2CH2CH3 | D) | CH3CH2CH3 | E) | CH3Cl |
|
|
|
34.
|
We can predict the solubility of a compound by looking at the sign of the
enthalpy of solution.
|
|
|
35.
|
What partial pressure of nitrogen gas is required in order for 0.00134 g of
the gas to dissolve in 13.1 mL of pure water? The Henry's law constant for nitrogen gas is
6.1 ´ 10–4 M
atm–1.
A) | 6.2 ´ 10–8 atm | B) | 1.7 ´ 10–1 atm | C) | 6.0 ´
100 atm | D) | 2.9 ´
10–8 atm | E) | 1.7 ´
10–2 atm |
|
|
|
36.
|
The solubility of a gas usually increases with increasing temperature.
|
|
|
37.
|
Liquid A and liquid B form a solution that behaves ideally according to
Raoult's law. The vapor pressures of the pure substances A and B are 233 torr and 135 torr,
respectively. Determine the vapor pressure over the solution if 1.21 moles of liquid A is added
to 5.30 moles of liquid B.
A) | 153 torr | B) | 188 torr | C) | 215
torr | D) | 760 torr | E) | 43.3 torr |
|
|
|
38.
|
A solution with a positive enthalpy of solution (DHsoln) is expected to show positive deviations from
Raoult's law.
|
|
|
39.
|
Adding salt to water decreases the freezing point of the water since it lowers
the vapor pressure of the ice.
|
|
|
40.
|
A cucumber is placed in a concentrated salt solution. What will most likely
happen?
A) | Water will flow from the cucumber to the solution. | B) | Water will flow from
the solution to the cucumber. | C) | Salt will flow into the
cucumber. | D) | Salt will precipitate out. | E) | No change will
occur. |
|
|
|
41.
|
Osmotic pressure depends on all but which of the following?
A) | atmospheric pressure | B) | the molarity of the
solution | C) | temperature | D) | the ratio of moles of solute to solution
volume | E) | none of these |
|
|
|
42.
|
Calculate the mole fraction of H2SO4 in 9.61 M
H2SO4. The density of the solution is 1.520 g/mL.
|
|
|
43.
|
A chemist is given a white solid that is suspected of being pure cocaine (molar
mass = 303.35 g/mol). When 1.22 g of the solid is dissolved in 15.60 g of benzene, the freezing point
is lowered by 1.32°C. The molar mass is calculated from these data to be 303 g. Assuming the
following uncertainties, can the chemist be sure the substance is not codeine (molar mass 299.36)?
Kf for benzene is
5.12°C/m.
Uncertainties
Mass of solid = ±0.01
g
Mass of
benzene = ±0.01
g
DT (freezing point lowering) =
±0.04°C
Kf =
±0.01
Support your answer with calculations.
|
|
|
44.
|
Calculate both the boiling point and the freezing point if 46.0 g of glycerol,
C3H5(OH)3, is dissolved in 500.0 g of H2O.
|
|
|
45.
|
Which of the following statements is/are true?
I. Supersaturated solutions
are very stable
II. The solubility of gases in liquids increases as the temperature is
raised
III. The solubility of gases in liquids is independent of the external pressure
A) | I and II only | B) | I and III only | C) | II and III
only | D) | II only | E) | none are true |
|
|
|
46.
|
Which of these solutions 0.1 m NaCl, 0.15 m glucose, 0.1 m CaCl2
would have
I. the highest vapor pressure
II. the highest boiling point
A) | 0.1 m CaCl2, 0.1 m CaCl2 | B) | 0.15 m glucose, 0.1
m CaCl2 | C) | 0.1 m CaCl2, 0.15 m
glucose | D) | 0.15 m glucose, 0.15 m glucose | E) | 0.1 m NaCl, 0.1 m
CaCl2 |
|
|
|
47.
|
The reaction 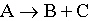 is second order in A. When
[A] 0 = 0.100 M, the reaction is 20.0% complete in 35.9 minutes. Calculate
the value of the rate constant (in L/min·mol). A) | 6.96 ´ 10–2 | B) | 5.57 ´ 10–4 | C) | 1.57 | D) | 1.11 | E) | none of these |
|
|
|
The following questions refer to the reaction 2A 2 + B 2
® 2C. The following mechanism has been proposed: | | step 1 (very slow) | | A2 + B2 ® R + C | | | step 2 (slow) | | A2 + R ® C | | | | |
|
|
|
48.
|
According to collision theory, the activated complex that forms in step 1 could
have which of the following structures? (The dotted lines represent partial bonds.)
|
|
|
49.
|
The rate constant k is dependent on | I. | the concentration of the
reactant | | II. | the
nature of the reactants | | III. | the temperature | | IV. | the order of the reaction | | |
A) | none of these | B) | one of these | C) | two of
these | D) | three of these | E) | all of these |
|
|
|
50.
|
Which of the following statements best describes the condition(s) needed for a
successful formation of a product according to the collision model?
A) | The collision must involve a sufficient amount of energy, provided from the motion of
the particles, to overcome the activation energy. | B) | The relative orientation of the particles has
little or no effect on the formation of the product. | C) | The relative orientation of the particles has
an effect only if the kinetic energy of the particles is below some minimum
value. | D) | The relative orientation of the particles must allow for formation of the new bonds
in the product. | E) | The energy of the incoming particles must be above a certain minimum value, and the
relative orientation of the particles must allow for formation of new bonds in the
product. |
|
|
|
51.
|
Determine (a) the rate equation and (b) the rate constant for the hypothetical
reaction A + B ® C given the following initial
concentrations and initial rate data. | | | [A]0 | [B]0 | Initial Rate | | | Run # | (mol/L) | (mol/L) | (mol/L·s) | | | (1) | 0.100 | 0.100 | 0.18 | | | (2) | 0.100 | 0.200 | 0.36 | | | (3) | 0.200 | 0.200 | 1.44 | | | | | |
|
|
|
A reaction represented by the equation was studied at a specific temperature and
the following data were
collected:
3O 2 ( g) ® 2O 3 ( g) Time
(seconds) | Total pressure
(atm) | 0 | 1.000 | 46.89 | 0.9500 | 98.82 | 0.9033 | 137.9 | 0.8733 | 200.0 | 0.8333 | 286.9 | 0.7900 | 337.9 | 0.7700 | 511.3 | 0.7233 | | |
|
|
|
52.
|
How many seconds would it take for the total pressure to be 0.7133 atm?
|
|
|
For the reaction aA ® Products, use the
following choices
a) zero order in A
b) first order in A
c) second order
in A
d) a, b, c
e) none of the above
|
|
|
53.
|
The rate is constant over time.
|