|
|
|
1.
|
Charles's law states that:
A) | Equal amounts of gases occupy the same volume at constant temperature and
pressure. | B) | The volume of a fixed amount of gas is inversely proportional to its pressure at
constant temperature. | C) | The volume of a fixed amount of gas is directly
proportional to its temperature in Kelvin at constant pressure. | D) | The total pressure
of a mixture of gases is the simple sum of the partial pressure of all of the gaseous
compounds. | E) | The rates of effusion of gases are inversely proportional to the square roots of
their molar masses. |
|
|
|
2.
|
You are holding four identical balloons each containing 10.0 g of a different
gas. The balloon containing which gas is the largest balloon?
A) | H2 | B) | He | C) | Ne | D) | O2 | E) | All have the same
volume. |
|
|
|
3.
|
Which of the following is the best qualitative graph of P versus molar
mass of a 1-g sample of different gases at constant volume and temperature?
|
|
|
4.
|
The diffusion of a gas is faster than the effusion of a gas.
|
|
|
5.
|
The van der Waals equation, nRT = [P +
a(n/V)2] (V – nb), incorporates corrections to the
ideal gas law in order to account for the properties of real gases. One of the corrections accounts
for
A) | the possibility of chemical reaction between molecules | B) | the finite volume of
molecules | C) | the quantum behavior of molecules | D) | the fact that average kinetic energy is
inversely proportional to temperature | E) | the possibility of phase changes when the
temperature is decreased or the pressure is increased |
|
|
|
6.
|
Of the following real gases, which would be expected to have the lowest van der
Waals correction for intermolecular attractions?
A) | H2 | B) | Cl2 | C) | NH3 | D) | O2 | E) | not enough
information to determine |
|
|
|
7.
|
Which of the following pollutant gases is not produced directly in a combustion
engine?
|
|
|
8.
|
For the reaction H2O(l) ®
H2O(g) at 298 K and 1.0 atm, DH is more positive
than DE by 2.5 kJ/mol. This quantity of energy can be considered to
be
A) | the heat flow required to maintain a constant temperature | B) | the work done in
pushing back the atmosphere | C) | the difference in the H–O bond energy in
H2O(l) compared to H2O(g) | D) | the value of DH itself | E) | none of these |
|
|
|
9.
|
Consider the
reaction
H 2( g) + 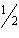 O 2( g) ® H 2O( l) DH° = –286 kJ Which of the following is true? A) | The reaction is exothermic. | B) | The reaction is
endothermic. | C) | The enthalpy of the products is less than that of the reactants. | D) | Heat is absorbed by
the system. | E) | Both A and C are true. |
|
|
|
10.
|
All of the following statements about the greenhouse effect are true
except:
A) | It occurs only on earth. | B) | The molecules H2O and CO2
play an important role in retaining the atmosphere's heat. | C) | Low humidity allows
efficient radiation of heat back into space. | D) | The carbon dioxide content of the atmosphere is
quite stable. | E) | A and D |
|
|
|
11.
|
Which of the following is not being considered as an energy source for
the future?
A) | ethanol | B) | methanol | C) | seed
oil | D) | shale oil | E) | carbon dioxide |
|
|
|
12.
|
Consider the following data: | | DH° (kJ) | Ca(s) + 2C(graphite) ®
CaC2(s) | –62.8 | Ca( s) + 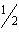 O 2( g) ® CaO( s) | –635.5 | CaO(s) + H2O(l) ®
Ca(OH)2(aq) | –653.1 | C 2H 2( g) + 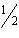 O 2( g) ® 2CO 2( g) +
H 2O( l) | –1300 | C(graphite) + O2(g) ®
CO2(g) | –393.51 | | |
Use Hess’ law
to find the change in enthalpy at 25°C for the following
equation:
CaC 2( s) +
2H 2O( l) ® Ca(OH) 2( aq) +
C 2H 2( g)
|
|
|
13.
|
All matter exhibits either particulate or wave properties exclusively.
|
|
|
14.
|
When an electron in a 2p orbital of a particular atom makes a transition
to the 2s orbital, a photon of approximate wavelength 629.1 nm is emitted. The energy
difference between these 2p and 2s orbitals is
A) | 3.16 ´ 10–28 J | B) | 3.16 ´ 10–19 J | C) | 3.16 ´
10–17 J | D) | 1.25 ´
10–31 J | E) | none of these |
|
|
|
15.
|
Bohr's model correctly describes the hydrogen atom and other small
atoms.
|
|
|
16.
|
The number of orbitals having a given value of l is equal to
A) | 2l + 1 | B) | 2n + 2 | C) | 3l | D) | l +
ml | E) | the number of lobes in each
orbital |
|
|
|
17.
|
The magnetic quantum number is related to the orientation of the orbital in
space relative to the other orbitals in the atom.
|
|
|
18.
|
The size of an orbital is arbitrarily defined.
|
|
|
19.
|
Which of the following atoms or ions has three unpaired electrons?
|
|
|
20.
|
Which of the following atoms has three electrons in p orbitals in its
valence shell?
A) | Ba | B) | Ga | C) | V | D) | Bi | E) | none of
these |
|
|
|
21.
|
For which of the following elements does the electron configuration for the
lowest energy state show a partially filled d orbital?
|
|
|
22.
|
When electron configurations differ from expected, it is because orbitals want
to be half-filled.
|
|
|
23.
|
Copper exhibits the expected electron configuration.
|
|
|
24.
|
Which of the following atoms would have the largest second ionization
energy?
|
|
|
25.
|
Which of the following statements is false?
A) | A sodium atom has a smaller radius than a potassium atom. | B) | A neon atom has a
smaller radius than an oxygen atom. | C) | A fluorine atom has a smaller first ionization
energy than an oxygen atom. | D) | A cesium atom has a smaller first ionization
energy than a lithium atom. | E) | All are true. |
|
|
|
26.
|
Photogray lenses incorporate small amounts of silver chloride in the glass of
the lens. The following reaction occurs in the light, causing the lenses to
darken:
AgCl
® Ag + Cl
The enthalpy change for this reaction is 3.10 ´ 102 kJ/mol. Assuming all this energy is supplied by light,
what is the maximum wavelength of light that can cause this reaction?
|
|
|
27.
|
The __________ quantum number is related to the size and energy of the
orbital.
|
|
|
Given the following electronic configuration of neutral atoms, identify the
element and state the number of unpaired electrons in its ground state:
|
|
|
28.
|
[Ne]3s23p5
|
|
|
29.
|
[Ar]4s13d10
|
|
|
30.
|
In general, the ionization energy and electron affinity involve more energy from
__________ (left to right or right to left) in a period of the periodic table. Why?
|
|
|
Choose the atom or ion using a periodic table.
|
|
|
31.
|
Larger first ionization energy, C or N
|
|
|
32.
|
When a metal reacts with a nonmetal a covalent bond is formed.
|
|
|
33.
|
In the gaseous phase, which of the following diatomic molecules would be the
most polar?
A) | CsF | B) | CsCl | C) | NaCl | D) | NaF | E) | LiF |
|
|
|
34.
|
Based on electronegativity differences, which of the following is most likely to
be ionic?
A) | CaF2 | B) | Br2 | C) | BH3 | D) | NO | E) | CF4 |
|
|
|
35.
|
Which of the following has the smallest radius?
|
|
|
36.
|
Which of the following pairs is isoelectronic?
A) | Li+ and K+ | B) | Na+ and Ne | C) | I–
and Cl– | D) | S2– and Ne | E) | Al3+ and
B3+ |
|
|
|
37.
|
The size in a series of isoelectronic ions increases as the nuclear charge
increases.
|
|
|
38.
|
Which of the following ionic compounds has the smallest lattice energy (i.e.,
the lattice energy least favorable to a stable lattice)?
A) | LiF | B) | CsI | C) | NaCl | D) | BaO | E) | MgO |
|
|
|
39.
|
Which of the following statements concerning lattice energy is
false?
A) | It is often defined as the energy released when an ionic solid forms from its
ions. | B) | MgO has a larger lattice energy than NaF. | C) | The lattice energy
for a solid with 2+ and 2– ions should be two times that for a solid with 1+ and 1–
ions. | D) | MgO has a larger lattice energy than LiF. | E) | All of these are
true. |
|
|
|
40.
|
Which of the following Lewis structures best describes BF3?
|
|
|
41.
|
Which has the greater N–O bond length, NO2– or
NO3–?
A) | NO2– | B) | NO3– | C) | The bond lengths are the
same. | D) | More information is needed. | E) | None of these
(A-D). |
|
|
|
42.
|
Choose the electron dot formula that most accurately describes the bonding in
CS2. (Hint: Consider formal charges.)
|
|
|
43.
|
Which of the following is not a valid resonance structure for
N3–?
A) |  | B) | 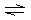 | C) | 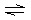 | D) | 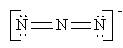 | E) | all are correct |
|
|
|
44.
|
Which of the following molecules has a dipole moment?
A) | CH4 | B) | CCl4 | C) | CO2 | D) | SO2 | E) | none of
these |
|
|
|
45.
|
Which of the following is the correct order for molecules from most to least
polar?
A) | CH4 > CF2Cl2 > CF2H2
> CCl4 > CCl2H2 | B) | CH4 > CF2H2
> CF2Cl2 > CCl4 >
CCl2H2 | C) | CF2Cl2 >
CF2H2 > CCl2H2 > CH4 =
CCl4 | D) | CF2H2 > CCl2H2 >
CF2Cl2 > CH4 = CCl4 | E) | CF2Cl2 > CF2H2 > CCl4
> CCl2H2 > CH4 |
|
|
|
Select the correct molecular structure for the given species from the choices
below:
|
|
|
46.
|
PF6–
A) | pyramidal | B) | tetrahedral | C) | square
planar | D) | octahedral | E) | none of these |
|
|
|
Select the correct molecular structure for the given species from the choices
below:
|
|
|
47.
|
I3–
A) | linear | B) | trigonal planar | C) | tetrahedral | D) | bent | E) | none of
these |
|
|
|
48.
|
ClF2+
A) | linear | B) | trigonal planar | C) | tetrahedral | D) | bent | E) | none of
these |
|
|
|
49.
|
The shape of a carbon dioxide molecule is linear.
|
|
|
50.
|
The ability of an atom in a molecule to attract shared electrons to itself is
called __________.
|
|
|
51.
|
The __________ of a molecule shows how the valence electrons are arranged among
the atoms in the molecule.
|
|
|
For each of the following compounds: |
a) | Draw the Lewis structure. | | b) | Give the shape of the molecule. | | c) | Indicate the polarity of the
molecule. | | |
|
|
|
52.
|
ICl4–
|
|
|
53.
|
Which choice has the bonds listed in the order of INCREASING bond energy?
A) | HF < HCl < HBr | B) | C-O < C=O < CºO | C) | F2 < Cl2 <
Br2 | D) | N2 < CC bond in C2H4 < CC Bond in
C2H6 | E) | all the same |
|