Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best
completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Which of the following is true about a system at equilibrium?
A) | The concentration(s) of the reactant(s) is equal to the concentration(s) of the
product(s). | B) | No new product molecules are formed. | C) | The concentration(s) of reactant(s) is constant
over time. | D) | The rate of the reverse reaction is equal to the rate of the forward reaction and
both rates are equal to zero. | E) | None of the above (A-D) is
true. |
|
|
|
Consider the following equilibrium: H 2( g) +
I 2( s)  2HI( g)
|
|
|
2.
|
Which of the following statements about the equilibrium is false?
A) | If the system is heated, the right side is favored. | B) | This is a
heterogeneous equilibrium. | C) | If the pressure on the system is increased by
changing the volume, the left side is favored. | D) | Adding more H2(g) increases
the equilibrium constant. | E) | Removing HI as it forms forces the equilibrium
to the right. |
|
|
|
3.
|
For the equilibrium
system: CO 2( g) + H 2( g)  CO( g) + H 2O( g) 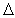 H H = +42 kJ/mol K equals 1.6 at 1260 K. If
0.15 mol each of CO 2, H 2, CO, and H 2O (all at 1260 K) were
placed in a 1.0-L thermally insulated vessel that was also at 1260 K, then as the system came to
equilibrium: A) | The temperature would decrease and the mass of CO2 would
increase. | B) | The temperature would decrease and the mass of CO2 would
decrease. | C) | The temperature would remain constant and the mass of CO2 would
increase. | D) | The temperature would increase and the mass of CO2 would
increase. | E) | The temperature would increase and the mass of CO2 would
decrease. |
|
|
|
4.
|
Initially 2.0 moles of N 2( g) and 4.0 moles of
H 2( g) were added to a 1.0-liter container and the following reaction then
occurred:
3H 2( g) + N 2( g)  2NH 3( g) The equilibrium concentration of
NH 3( g) = 0.55 moles/liter at 700.°C. The value for K at
700.°C for the formation of ammonia is: A) | 1.0 ´ 10–1 | B) | 5.5 ´ 10–2 | C) | 5.5 ´
10–3 | D) | 3.0 ´
10–1 | E) | none of these |
|
|
|
Given the equation 2A( g)  2B( g) +
C( g). At a particular temperature, K = 1.6 ´ 10 4.
|
|
|
5.
|
Raising the pressure by lowering the volume of the container will
A) | cause [A] to increase | B) | cause [B] to
increase | C) | have no effect | D) | cannot be determined | E) | none of the
above |
|
|
|
6.
|
Consider the endothermic reaction 2 BrCl(g) D
Br2(g) + Cl2(g). What will be the effect on the equilibrium of
a) changing the volume at constant
temperature?
b) increasing the temperature at constant volume
A) | a) equilibrium shifts towards products, b) equilibrium
shifts towards products. | B) | a) equilibrium shifts towards reactants,
b) equilibrium shifts towards products. | C) | a) equilibrium
shifts towards products, b) equilibrium shifts towards
reactants. | D) | a) no change in the equilibrium,
b) equilibrium shifts towards products. | E) | a) no change in the
equilibrium, b) equilibrium shifts
towards reactants. |
|
|
|
7.
|
Consider the reaction, which is exothermic as written, PCl5(g) D PCl3(g) + Cl2(g). Which of the following changes
would result in the production of LESS Cl2(g)?
I.
adding PCl3(g)
II. removing
PCl3(g)
III. reducing the volume of the
container
IV. removing
PCl5(g)
V. increasing the
temperature
VI. increasing the volume of the
container
VII. adding
PCl5(g)
VIII. reducing the
temperature
IX. adding a suitable catalyst
A) | II, III, VII, VIII | B) | I, III, IV, V | C) | I, III, IV,
VIII | D) | I, V, VI, VII | E) | I, III, IV, V,
IX |
|
|
|
8.
|
Consider the reaction HNO 2( aq) + H 2O( l)  H 3O +( aq) + NO 2–( aq).
Which species is a conjugate base? A) | HNO2(aq) | B) | H2O(l) | C) | H3O+(aq) | D) | NO2–(aq) | E) | two of
these |
|
|
|
9.
|
In which of the following reactions does the
H2PO4– ion act as an acid?
A) | H3PO4 + H2O ®
H3O+ + H2PO4– | B) | H2PO4– + H2O ® H3O+ +
HPO42– | C) | H2PO4– +
OH– ® H3PO4 +
O2– | D) | The ion cannot act as an
acid. | E) | Two of these. |
|
|
|
The following three equations represent equilibria that lie far to the
right. | | HNO3(aq) + CN–(aq)  HCN(aq) + NO3–(aq)
HCN(aq) + NO3–(aq) | | | HCN(aq) +
OH–(aq)  H2O(l) +
CN–(aq) H2O(l) +
CN–(aq) | | | | H2O(l) +
CH3O–(aq)  CH3OH(aq) + OH–(aq)
CH3OH(aq) + OH–(aq) | | | |
|
|
|
10.
|
Identify the strongest acid.
A) | HCN | B) | HNO3 | C) | H2O | D) | OH– | E) | CH3OH |
|
|
|
11.
|
For the stepwise dissociation of aqueous H3PO4, which of
the following is not a conjugate acid–base pair?
A) | HPO42– and
PO43– | B) | H3PO4 and
H2PO4– | C) | H2PO4–
and HPO42– | D) | H2PO4–
and PO43– | E) | H3O+ and
H2O |
|
|
|
12.
|
Which of the following species is present in the greatest concentration in a
0.100 M H2SO4 solution in H2O?
A) | H3O+ | B) | HSO4– | C) | H2SO4 | D) | All species are in
equilibrium and therefore have the same concentration. | E) | SO42– |
|
|
|
13.
|
The sodium salt, NaA, of a weak acid is dissolved in water; no other substance
is added. Which of these statements (to a close approximation) is true?
A) | [H+] = [A–] | B) | [H+] = [OH–] | C) | [A–] =
[OH–] | D) | [HA] =
[OH–] | E) | none of these |
|
|
|
14.
|
Which of the following would give the highest pH when dissolved in water to form
a 0.10 M solution?
A) | a strong acid | B) | a weak acid | C) | the potassium salt
of a weak acid | D) | the potassium salt of a strong acid | E) | the ammonium salt of a strong
acid |
|
|
|
Select the answer that best describes an aqueous solution made from each of the
following substances:
|
|
|
15.
|
solid sodium nitrate (NaNO3)
A) | acidic | B) | basic | C) | neutral | D) | cannot tell | E) | none of these
(A-D) |
|
|
|
16.
|
solid aluminum chloride (AlCl3)
A) | acidic | B) | basic | C) | neutral | D) | cannot tell | E) | none of these
(A-D) |
|
|
|
17.
|
Which of the following correctly labels the salts? | HF (Ka = 7.2 ´ 10–4) | NH3
(Kb = 1.8 ´ 10–5) | HCN (Ka = 6.2 ´ 10–10) | | | |
A) | NaCN = acidic, NH4F = basic, KCN = neutral | B) | NaCN = acidic,
NH4F = neutral, KCN = basic | C) | NaCN = basic, NH4F = basic, KCN=
neutral | D) | NaCN = basic, NH4F = neutral, KCN = basic | E) | NaCN = basic,
NH4F = acidic, KCN = basic |
|
|
|
18.
|
Which of the following is the correct order for increasing pHs for equimolar
solutions of HNO3, KCl, NH4Cl, KOH, and
NaC2H3O2? (Ka for
HC2H3O2 is 1.80 ´ 10–5, Ka for
NH4+ is 5.56 ´ 10–10).
A) | KCl, NH4Cl, HNO3, KOH,
NaC2H3O2 | B) | HNO3, KCl, NH4Cl, KOH,
NaC2H3O2 | C) | NH4Cl, HNO3, KCl, KOH,
NaC2H3O2 | D) | HNO3, NH4Cl, KCl,
NaC2H3O2, KOH | E) | none of these |
|
|
|
19.
|
Which factor listed below is most important in determining the strength of an
oxyacid?
A) | the size of the molecule | B) | the ability of the molecule to change atomic
orientation | C) | the identity of the central atom in the molecule | D) | the number of oxygen
atoms present in the molecule | E) | none of these |
|
|
|
20.
|
Which of the following would produce a basic aqueous solution?
A) | P4O10 | B) | KCl | C) | CO2 | D) | NH4Cl | E) | none of
these |
|
|
|
21.
|
Which of the following species cannot act as a Lewis base?
A) | O2– | B) | OH– | C) | CH4 | D) | H2S | E) | NH3 |
|
|
|
22.
|
Which of the following species cannot act as a Lewis acid?
|
|
|
23.
|
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
A) | A solution of ammonium chloride will have a pH less than 7. | B) | A solution of
potassium bromide will have a pH of 7. | C) | A solution of cobalt(II) chloride will have a
pH less than 7. | D) | Given that the Kb of ammonia is 1.8 x 10-5 and the
Ka of hydrofluoric acid is 6.8 x 10-4, a solution of ammonium fluoride will
have a pH of less than 7. | E) | A solution of sodium phosphate will have a pH
of less than 7. |
|
|
|
24.
|
Describe the pH of the following salts? NaF, NH4Cl, KI,
NH4F
A) | acidic, basic, neutral, cannot tell without further information | B) | neutral, acidic,
neutral, cannot tell without further information | C) | neutral, acidic, neutral,
neutral | D) | basic, acidic, neutral, cannot tell without further information | E) | basic, acidic,
neutral, neutral |
|
|
|
25.
|
A weak acid, HF, is in solution with dissolved sodium fluoride, NaF. If HCl is
added, which ion will react with the extra hydrogen ions from the HCl to keep the pH from
changing?
A) | OH– | B) | Na+ | C) | F– | D) | Na– | E) | none of
these |
|
|
|
26.
|
Which of the following solutions will be the best buffer at a pH of 9.26?
(Ka for HC2H3O2 is 1.8 ´ 10–5, Kb for NH3 is
1.8 ´ 10–5).
A) | 0.10 M HC2H3O2 and 0.10 M Na
C2H3O2 | B) | 5.0 M HC2H3O2
and 5.0 M Na C2H3O2 | C) | 0.10 M
NH3 and 0.10 M NH4Cl | D) | 5.0 M NH3 and 5.0 M
NH4Cl | E) | 5.0 M HC2H3O2 and 5.0 M
NH3 |
|
|
|
You have two buffered solutions. Buffered solution 1 consists of 5.0 M
HOAc and 5.0 M NaOAc; buffered solution 2 is made of 0.050 M HOAc and 0.050 M
NaOAc.
|
|
|
27.
|
How do the pHs of the buffered solutions compare?
A) | The pH of buffered solution 1 is greater than that of buffered solution
2. | B) | The pH of buffered solution 2 is greater than that of buffered solution
1. | C) | The pH of buffered solution 1 is equal to that of buffered solution
2. | D) | Cannot be determined without the Ka values. | E) | None of these
(A-D). |
|
|
|
28.
|
A 75.0-mL sample of 0.0650 M HCN
(Ka = 6.2 ´ 10–10) is titrated with 0.65 M NaOH.
What volume of 0.65 M NaOH is required to reach the stoichiometric point?
A) | 750. mL | B) | 7.50 mL | C) | 3.75
mL | D) | 75.0 mL | E) | cannot determine without knowing the pH at the
stoichiometric point |
|
|
|
Consider the following information about the diprotic acid, ascorbic acid.
(H 2As for short, molar mass 176.1) H 2As 
HAs – + H + p Ka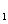 = 4.10 ( Ka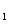 = 7.9 ´ 10 –5) HAs –  As 2– + H +
p Ka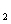 = 11.79 ( Ka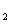 = 1.6 ´ 10 –12) The
titration curve for disodium ascorbate, Na 2As, with standard HCl is shown below: 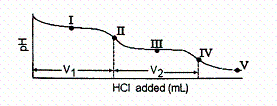
|
|
|
29.
|
What is the pH at point III?
A) | 4.10 | B) | 7.95 | C) | 11.79 | D) | 12.39 | E) | none of
these |
|
|
|
30.
|
Which of the following is a major species present at point IV?
A) | H2As | B) | HAs– | C) | As2– | D) | H+ | E) | none of
these |
|
|
|
31.
|
Assume an indicator works best when the equivalence point of a titration comes
in the middle of the indicator range. Which indicator would be best for the following
titration?
0.100 M HOCl (Ka = 3.5 ´ 10–8) + 0.100 M NaOH
A) | crystal violet (0.2 - 1.8) | B) | phenolphthalien (8.2 -
10.0) | C) | methyl orange (3.2 - 4.4) | D) | thymolphthalein (9.5 -
10.5) | E) | cresol red (7.0 - 8.8) |
|
|
|
32.
|
In the titration of a weak acid HA with 0.100 M NaOH, the stoichiometric
point is known to occur at a pH value of approximately 10. Which of the following indicator acids
would be best to use to mark the endpoint of this titration?
A) | indicator A, Ka = 10–14 | B) | indicator B,
Ka = 10–11 | C) | indicator C, Ka =
10–8 | D) | indicator D, Ka =
10–6 | E) | none of these |
|
|
|
33.
|
In the titration of a weak acid, HA, with a sodium hydroxide solution of
approximately the same concentration, the stoichiometric point occurs at pH = 9.5. Which of the
following weak acid indicators would be best suited to mark the endpoint of this titration?
A) | indicator A, Ka = 10–11 | B) | indicator B,
Ka = 10–13 | C) | indicator C, Ka =
10–9 | D) | indicator D, Ka =
10–7 | E) | indicator E, Ka =
10–5 |
|
|
|
34.
|
Which of the following mixtures would be classified as a buffer solution?
A) | 50 mL of 0.100 M HCl and 50 mL of 0.100 M KCl | B) | 50 mL of 0.100 M
CH3COOH and 55 mL of 0.100 M NaOH | C) | 50 mL of 0.100 M CH3COOH and 25 mL
of 0.100 M NaOH | D) | 50 mL of 0.100 M CH3COOH and 0.500 mL of 0.000100 M
NaOH | E) | 50 mL of 0.100 M CH3COOH and 55 mL of 0.100 M
HCl |
|
|
|
35.
|
Solubility Products ( Ksp) BaSO4 | 1.5 ´ 10–9 | CoS | 5.0 ´ 10–22 | PbSO4 | 1.3 ´ 10–8 | AgBr | 5.0 ´ 10–13 | BaCO3 | 1.6 ´ 10–9 | | |
Which of the following
compounds is the most soluble (in moles/liter)? A) | BaSO4 | B) | CoS | C) | PbSO4 | D) | AgBr | E) | BaCO3 |
|
|
|
36.
|
Which of the following solid salts is more soluble in 1.0 M H+ than
in pure water?
A) | NaCl | B) | KCl | C) | FePO4 | D) | AgCl | E) | KNO3 |
|
|
|
37.
|
The best explanation for the dissolution of ZnS in dilute HCl is that:
A) | The zinc ion is amphoteric. | B) | The sulfide-ion concentration is decreased by
the formation of H2S. | C) | the sulfide-ion concentration is decreased by
oxidation to sulfur. | D) | the zinc-ion concentration is decreased by the
formation of a chloro complex. | E) | The solubility product of ZnCl2 is
less than that of ZnS. |
|
|
|
38.
|
Sodium chloride is added slowly to a solution that is 0.010 M in
Cu+, Ag+, and Au+. The Ksp values for the chloride
salts are 1.9 ´ 10–7, 1.6 ´ 10–10, and 2.0 ´ 10–13, respectively. Which compound will
precipitate first?
A) | CuCl | B) | AgCl | C) | AuCl | D) | All will precipitate at the same
time. | E) | Cannot be determined. |
|
|
|
39.
|
A 0.012-mol sample of Na2SO4 is added to 400 mL of each of
two solutions. One solution contains 1.5 ´ 10–3 M BaCl2; the other contains
1.5 ´ 10–3 M CaCl2.
Given that Ksp for BaSO4 = 1.5 ´ 10–9 and Ksp for CaSO4
= 6.1 ´ 10–5:
A) | BaSO4 would precipitate but CaSO4 would
not. | B) | CaSO4 would precipitate but BaSO4 would
not. | C) | Both BaSO4 and CaSO4 would precipitate. | D) | Neither
BaSO4 nor CaSO4 would precipitate. | E) | Not enough
information is given to determine if precipitation would occur. |
|
|
|
40.
|
What is the maximum concentration of carbonate ions that will precipitate
BaCO 3 but not MgCO 3 from a solution that is 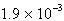 M M each in Mg 2+ and Ba 2+? For MgCO 3,
Ksp = 1.0 ´ 10 –15 and for BaCO 3,
Ksp = 2.6 ´ 10 –9. A) | 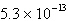 M M | B) | 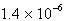 M
M | C) | 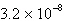 M M | D) | 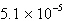 M
M | E) | None of these; MgCO3 will always precipitate before
BaCO3. |
|
|
|
41.
|
Which of the following solid salts should be more soluble in 1.0 M
NH3 than in water?
A) | Na2CO3 | B) | KCl | C) | AgBr | D) | KNO3 | E) | none of
these |
|
|
|
The following questions refer to the following system: 500.0 mL of 0.020
M Mn(NO 3) 2 are mixed with 1.0 L of 1.0 M
Na 2C 2O 4. The oxalate ion, C 2O 4, acts as a
ligand to form a complex ion with the Mn 2+ ion with a coordination number of two. | | Mn2+ +
C2O42–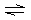 MnC2O4 MnC2O4 | | K1 = 7.9 ´ 103 | | | [Mn(C2O4)2]2–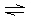 MnC2O4 + C2O42– MnC2O4 + C2O42– | | K2 = 1.26 ´ 10–2 | | | | |
|
|
|
42.
|
Find the equilibrium concentration of the
[Mn(C2O4)2]2– ion.
A) | 9.2 ´ 10–5
M | B) | 0.01 M | C) | 2.5 ´ 10–8 M | D) | 1.3 ´ 10–4 M | E) | 6.7 ´ 10–3 M |
|
|
|
43.
|
The cation M 2+ reacts with NH 3 to form a series of complex
ions as follows: | | M2+ + NH3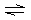 M(NH3)2+ M(NH3)2+ | K1 = 102 | | | M(NH3)2+ + NH3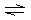 M(NH3)22+ M(NH3)22+ | K2 = 103 | | | M(NH3)22+ +
NH3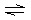 M(NH3)32+ M(NH3)32+ | K3 = 102 | | | |
A 1.0 ´ 10 –3 mol sample of M(NO 3) 2 is
added to 1.0 L of 15.0 M NH 3 ( Kb = 1.8 ´ 10 –5). Choose the dominant species in this
solution. A) | M2+ | B) | M(NH3)2+ | C) | M(NH3)22+ | D) | M(NH3)32+ | E) | M(NO3)2 |
|
|
|
44.
|
Given that the Ksp for calcium fluoride [CaF2]
is 3.2 x 10-15, which of the following describes a solution that is 2.00 x 10-5
M NaF and 2.00 x 10-5 M Ca(NO3)2?
A) | Q = 4 x 10-10 and there will be a precipitate formed | B) | Q = 8 x
10-10 and there will be a precipitate formed | C) | Q = 8 x
10-15 and there will be no precipitate formed | D) | Q = 1.3 x
10-13 and there will be a precipitate formed | E) | Q = 8 x
10-15 and there will be a precipitate formed |
|
True/False
Indicate whether the statement is
true or false.
|
|
|
Consider the reaction HOCl + F –  HF +
OCl –
|
|
|
1.
|
Assuming that the value for K in the above reaction is greater than 1,
this means that HF is a stronger acid than HOCl.
|
|
|
You have two buffered solutions. Buffered solution 1 consists of 5.0 M
HOAc and 5.0 M NaOAc; buffered solution 2 is made of 0.050 M HOAc and 0.050 M
NaOAc.
|
|
|
2.
|
Buffered solution 1 has a greater buffering capacity than buffered solution
2.
|
Short Answer
|
|
|
1.
|
Explain why 0.1 M NaCN is basic while 0.1 M NaNO3 is
neutral.
|
|
|
Determine whether the following oxides produce an acidic, basic, or neutral
solution when dissolved in water:
|
|
|
2.
|
K2O
|
|
|
3.
|
NO2
|
|
|
4.
|
Cl2O
|
|
|
5.
|
SO2
|